Welcome to my chemistry blog
Acids and bases are not something unfamiliar to us,we come across them on a day to day basis as a matter of fact they are present in our body controlling our bodily functions.But what exactly are they ?what makes an acid an acid? And how different is it from base? Does this mean we can categorise the items we encounter in our day to day life into acids and bases?
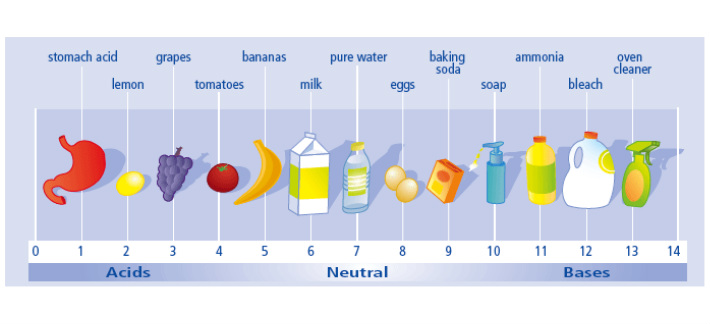
pH Scale
pH is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration. pH is a scale often used to specify acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Aqueous solutions at 25 degree Celsius with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic while those which pH greater than 7 are considered to be basic.pH 7 is defined as a neutral point.
pH Equation The equation used for calculating pH was proposed by Danish biochemist Soren Peter Lauritz Sorensen. And is given as

Side note : we also use litmus papers to know if a substance is acidic or basic.
Arrhenius theory
According to Arrhenius an acid is a substance that releases H+ ions in water.Eg- HCl. While a base is a substance that dissociates in water to give OH- ions.Eg NaOH.


However this was a very basic theory which had a lot of limitations some of which included
1) acids and bases must be in aqueous solutions this prevents use of other solvents like benzene. 2)Not all acid base reactions take place in solutions.For eg: Ammonia gas and chlorine gas produce ammonium chloride.
In order to over come all these limitations another theory was bought forward this was the Bronsted-Lowry acid base theory
Bronsted-Lowry acid base theory
According to this theory acid is a proton (H+) donor while base is a proton (H+) acceptor.
This theory also proposed the concept of conjugate acid base pairs,these are compounds which differ from each other only by one proton.Also if the acid is strong then it’s conjugate base will be weak and vice-versa.
This theory also introduced us to compounds like water which can act like both acids and bases they are called Amphoteric or amphiproteic.
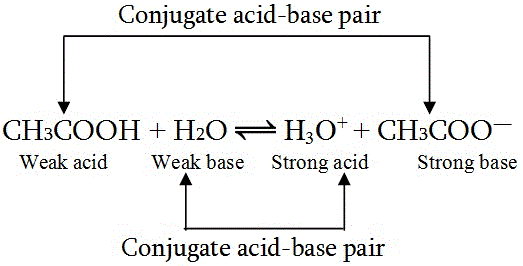
Dispite being better than Arrhenius theory, this theory also had limitations like it only talks about compounds that have protons in them so how to classify those compounds devoid of protons.
This leads us to our final theory of the post the Lewis acid base theory.
Lewis theory
According to this theory acids are those substances that can accept electron pairs while bases are those that can donate electron pairs.
This gives us a vast variety of examples which could be directly classified as acids and bases.
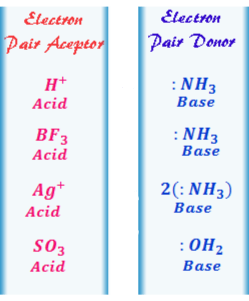
Lewis theory has generalized and included in his theory definitions of Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry theories. This theory is characterized by its simplicity
However this theory also has some limitations like how it doesn’t directly classify acids and bases based on their strengths.
In conclusion all these theories have helped us to future advance our knowledge of acids and bases and should receive a special mention for there simplistic approach.
So Goodbye from me until the next post

- Carbon nanotubes
- Chemistry of main group elements
- Non-Aqueous Solvents
- Applications of HSAB Principle #8
- Factors affecting acids and bases strength #7 (14-sept 2020)