Thursday 24-09-2020
Water is a universal solvent and easily available ,it hence has an incredible number of applications however there are instances when some reagents may react with water and also another unavoidable problem is non-polar molecules are insoluble in water.Thus came a need for other solvents which can be used in places where water cannot be used.
Solvents other than water
Solvents are classified into
a)protic solvent(Eg:HF,H2SO4,MeOH)
b)aprotic solvent(Eg:BrF4,N2O4)
c)co-ordinating solvent (Eg :MeCN,Me2CO)
A protic solvent undergoes self-ionisation to give protons which are solvated on the other hand an aprotic solvent undergoes self-ionisation without formation of protons.
Disadvantages of using non-aqueous solutions
They are limited
Expensive
Highly reactive
Acid base behaviour in non-aqueous solvents
Strengths of acids and bases
In acidic solvents like acetic acid,the extend of ionisation of a molecule like HCl is far less than that of ionisation of HCl in water.
Thus HCl behaves as a weak acid in acetic acid.However this solvent cannot differentiate basic strengths in other words all bases are strong in an acidic solvent.(Ammonia is as strong as a base as CH3OH)
Similarly in a basic solvent like ammonia , acetic acid is a strong base so is HCl, therefore all acids in a basic solvent are equally strong and there strengths cannot be differentiated .
Here ammonia is said to exhibit a leveling effect on the acid just as acetic acid exhibits a leveling effect on the base.
Leveling effect
The effect of solvent on the properties of acids and bases.i.e., the strength of a strong acid (or base) is limited or leveled by basicity(or acidity) of the solvent.

Differentiating effect
In acetic acid the extend of ionisation of hydrogen halides vary as follows
HI>HBr>HCl.Thus acetic acid shows differentiating effect on the acidic behaviour of the three halides unlike water where all three have the same extent of ionisation.The reason for HCl being a weak acid in acetic acid is because both acetic acid and HCl compete for protons and acetic acid being a poor proton acceptor does it with lessor efficiency thus making HCl a weaker acid in this medium.
This is the opposite of leveling effect and can be defined as an effect in which the acidity (or basicity) of acids(or bases) are differentiated by basicity (or acidity) of the solvent.
Strength of mineral acids can be determined on using acetic acid as the solvent the order is as follows
HNO3<HCl<H2SO4<HBr<HClO4
Let us now consider a few examples of leveling and differentiating of some bases
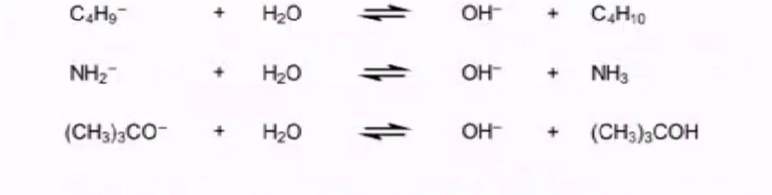
All of these bases completely deprotonate water to give OH- ,due to this the only basic species in the solution is OH- .
Thus despite the three bases being different in strength in water they all have the same basicity as there basicity is levelled down by basicity of water.
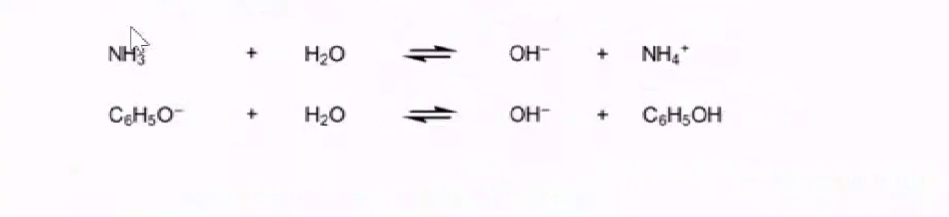
However in case of weak bases like ammonia and phenoxide as the cannot completely dissociate they cannot completely deprotonate water to OH- ions therefore in solution as only small part of water is deprotonated they largely remain as themselves thus water is not able to level the weak bases.
