21 September
1)In Hydrogen bonding – strong H bonding between atoms of HF,H20,NH3 etc is possible as donor atoms F,O,N are hard Lewis bases and they interact with hard Lewis acid H.
2)Linkage of ambidentate ligands to metal atoms
Considering an ambidentate ligand like SCN it can be S-bound to a metal or N-bound to a metal ,this choice is dependent of whether the metal is hard or soft . Therefore when metal is soft then it will be bound by S of SCN and if it’s hard it’s bound by N end of SCN.
Ex- hard Cr3+ binds with N end
And soft Pt2+ binds with S end
3) Symbiosis
When the hard or soft character of a metal ion is altered by attachment of other groups.Such an effect is called symbiosis.
Ex: Co(+3) is a hard acid and is expected to be N- bonded to SCN as seen in
[Co(NH3)5(NCS)](3-) but when 5 soft bases CN- are attached to Co(+3) then the hardness of this ion is reduced .Thus [Co(CN)5](2-)now behaves as a soft acid and prefers to bind with S end of SCN to form
[Co(CN)5(SCN)](-3).
4) HSAB principle can be used to predict the direction of inorganic reactions
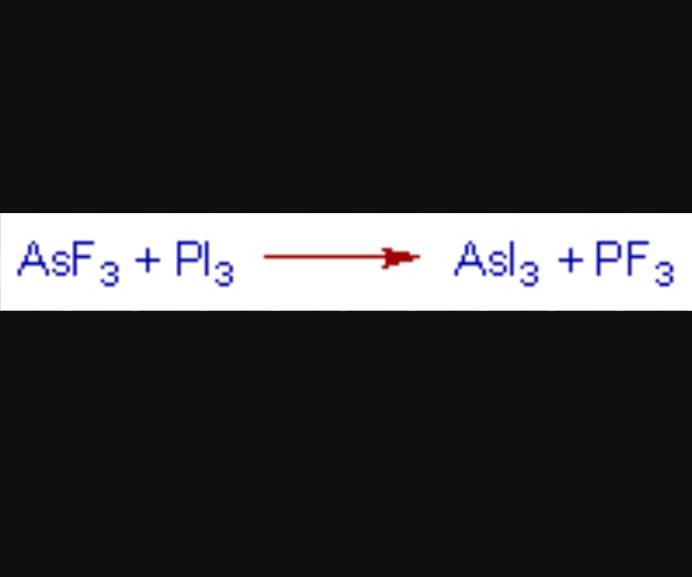
The reaction between AsF3 and PI3 is possible and proceeds to the right since As3+ is softer than P3+ and I- is softer than F-.
Although both As3+ and P3+ are soft but relatively As3+ is softer due to larger size.
5)Solubility in water
The compound formed due to soft acid-soft base combination is more covalent and less soluble in polar solvents like water. For example, Silver iodide, AgI is insoluble in water as it has covalent nature since it is the combination of soft acid, Ag+ and soft base, I-.
On the other hand, Lithium iodide, LiI is the result of a combination of Li+ (hard acid) and I- (soft base). Thus it is polar covalent and thus soluble in water.